The Challenge of Scaling Applications
A startup built a mobile app that suddenly went viral. Their servers crashed under the traffic surge.
The problem? Their infrastructure wasn’t designed to scale dynamically.
The solution? Serverless architectures, where applications automatically scale based on demand, reducing operational complexity and cost.
What is Serverless Architecture?
Serverless allows developers to run applications without managing infrastructure. The cloud provider handles scaling, provisioning, and maintenance.
Example: Instead of running a dedicated server for an API, a serverless function is triggered only when needed.
Key Benefits:
Auto-Scaling: Resources scale up and down instantly.
Cost-Efficient: Pay only for execution time (no idle costs).
No Server Management: Focus on code, not infrastructure.
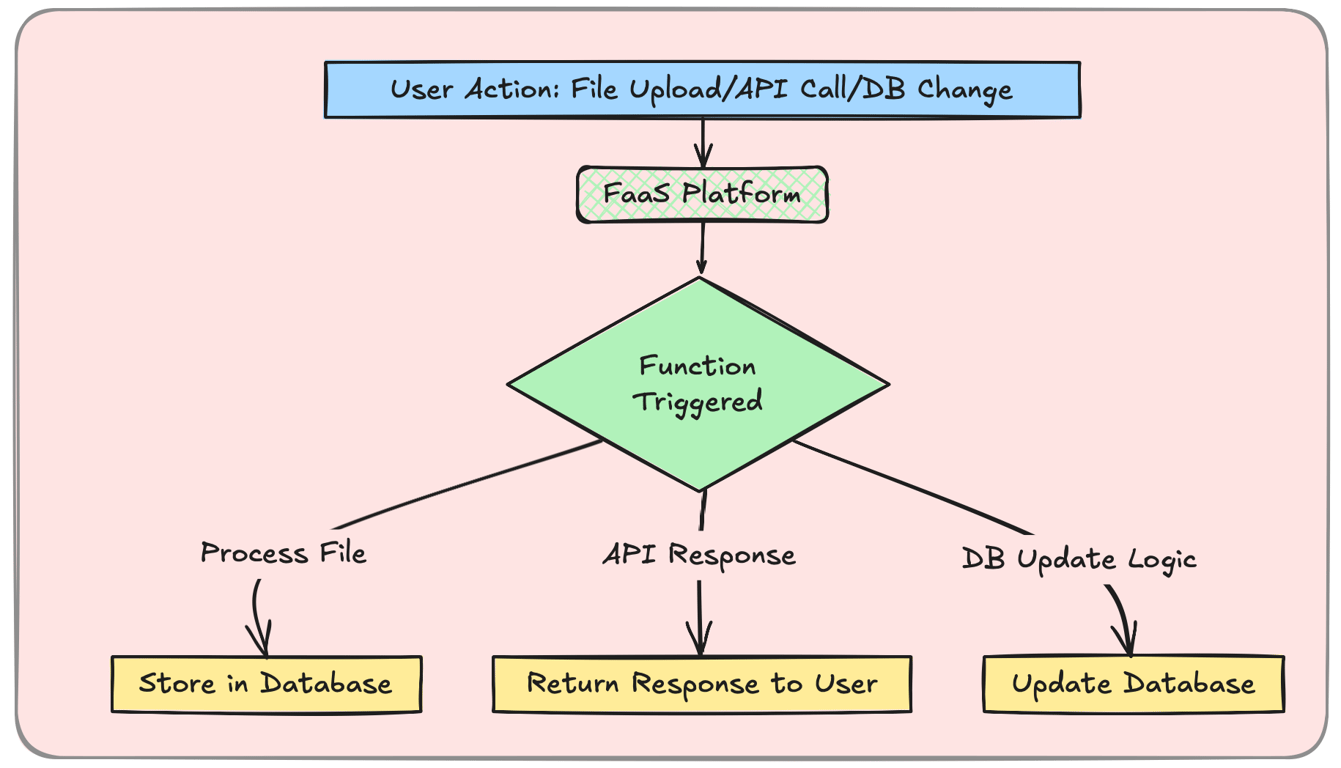
Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) – The Core of Serverless
FaaS enables developers to write small, independent functions that execute in response to events.
Example:
A function triggers when a user uploads a file.
Another function processes and stores the file in a database.
Event Sources for FaaS:
HTTP Requests – API calls trigger functions.
Database Changes – Functions react to new records.
File Uploads – Runs when files are added to cloud storage.
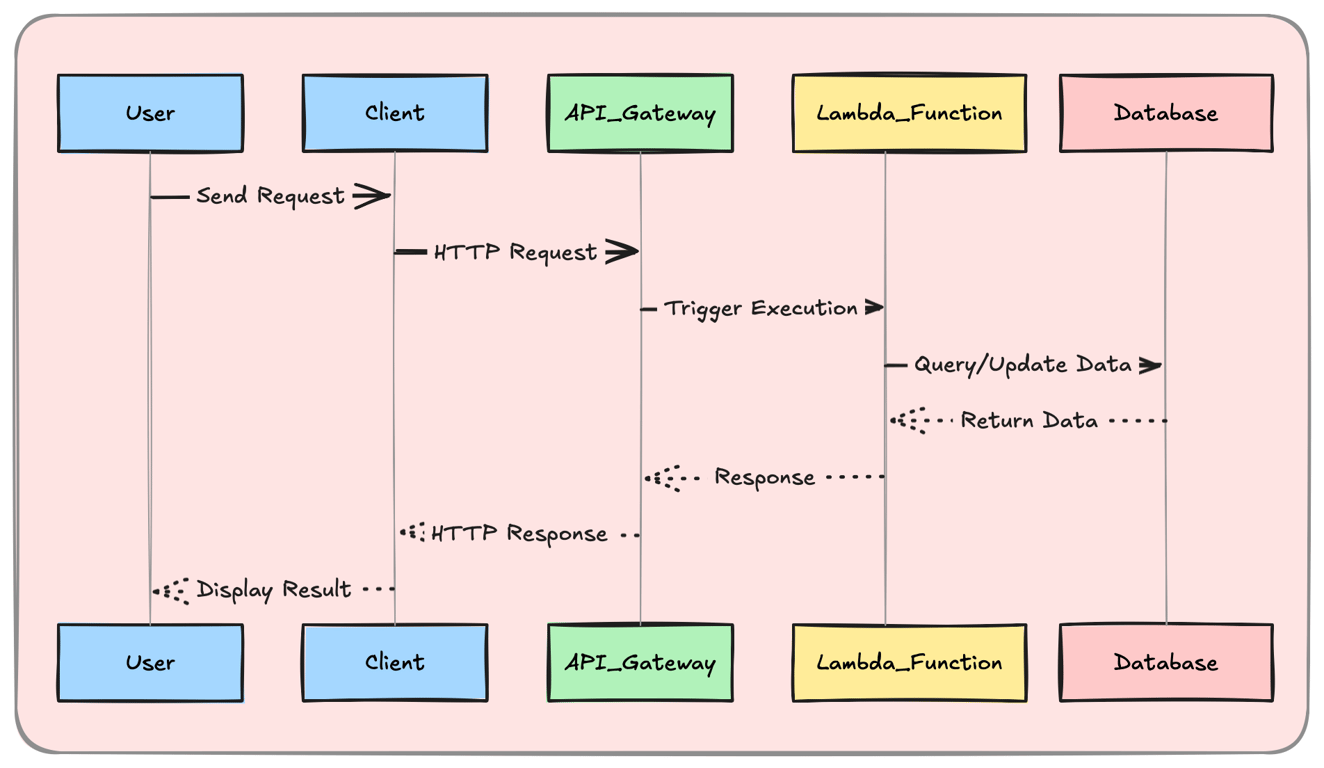
AWS Lambda – Serverless on AWS
AWS Lambda is a leading FaaS platform that runs code in response to events.
Key Features:
Supports multiple languages (Python, Node.js, Go, Java, etc.).
Integrates with AWS services (S3, DynamoDB, API Gateway).
Scales automatically based on incoming traffic.
Example Use Case:
A Lambda function processes payments when an order is placed.
Another Lambda function sends email notifications to users.
Google Cloud Functions – Serverless on GCP
Google Cloud Functions provide an event-driven, fully managed execution environment.
Key Features:
Deep integration with Google Cloud services (Firestore, Pub/Sub, BigQuery).
Supports multiple runtime environments (Node.js, Python, Go, Java).
Event-driven architecture triggers functions based on cloud events.
Example Use Case:
A function triggers when a user submits a form, storing data in Firestore.
Another function analyzes uploaded files in Cloud Storage.
Comparing AWS Lambda vs. Google Cloud Functions
Feature
AWS Lambda
Google Cloud Functions
Best For
General-purpose serverless workloads
GCP-native applications
Cold Start Time
Slightly higher
Faster
Integration
Strong AWS ecosystem
Tight GCP integration
Pricing Model
Pay-per-execution
Pay-per-execution
Real-World Use Cases
1. E-Commerce Platforms
AWS Lambda processes payments and generates invoices.
Google Cloud Functions triggers product recommendations in real-time.
2. IoT Applications
AWS Lambda analyzes IoT sensor data in real-time.
Google Cloud Functions processes alerts from IoT devices.
3. Data Processing & Automation
Serverless functions process uploaded files.
Log analysis and event-driven automation with FaaS.
Conclusion
Serverless architectures simplify application deployment, scaling, and cost management.
AWS Lambda is ideal for event-driven workloads in the AWS ecosystem.
Google Cloud Functions provide seamless integration with GCP services.
FaaS models enable developers to focus on code while the cloud handles infrastructure.
Next, we’ll explore Security in System Design – OAuth, JWT, TLS, Encryption, Rate-Limiting, Firewalls.


