The E-Commerce Checkout Bottleneck
A popular e-commerce site had a major issue. Customers placed orders, but payments sometimes failed, or confirmations were delayed.
The problem? The system processed everything synchronously, causing slowdowns.
The solution? Message queues and event-driven architectures, ensuring real-time, scalable, and efficient communication between services.
What is a Message Queue?
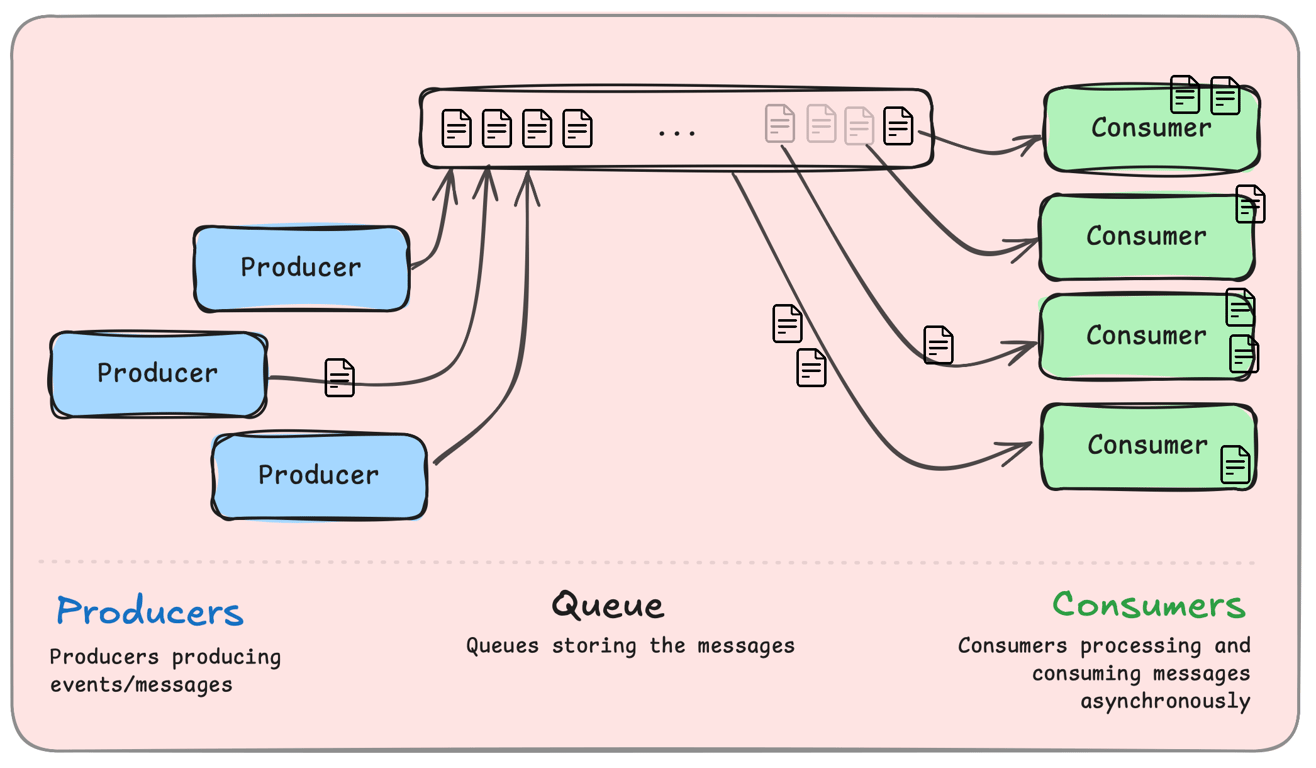
A message queue is a system that enables asynchronous communication by storing and forwarding messages between services.
How It Works:
A producer (e.g., checkout service) sends a message to the queue.
The queue temporarily stores the message.
A consumer (e.g., payment processor) retrieves and processes the message asynchronously.
This prevents service delays and ensures smooth execution.
What is an Event-Driven Architecture?
Event-driven architecture (EDA) is a design pattern where services react to events instead of making direct calls.
Example: When a user places an order, an event triggers inventory updates, payment processing, and shipping—without direct service dependencies.
Benefits:
Decoupling: Services operate independently.
Scalability: Easily handles high event loads.
Real-time Processing: Immediate responses to critical events.
Popular Message Queues & Event Streaming Platforms
1. Apache Kafka – Distributed Event Streaming
Kafka is a high-throughput, fault-tolerant event streaming platform.
Key Features:Publish-subscribe model – Multiple consumers can process the same event.
Event retention – Stores messages for replayability.
Scalable & fault-tolerant – Handles millions of messages per second.
Use Cases:
Logging and real-time analytics.
Clickstream processing for user behavior tracking.
Fraud detection in banking systems.

2. RabbitMQ – Lightweight & Reliable Message Broker
RabbitMQ is a robust message broker using a queue-based model.
Key Features:Supports multiple messaging patterns (direct, fanout, topic-based routing).
Message acknowledgment & durability – Prevents data loss.
Flexible queuing mechanisms for priority-based processing.
Use Cases:
Background job processing (e.g., sending emails asynchronously).
Order processing pipelines in e-commerce.
Task distribution across multiple workers.

3. Amazon SQS – Fully Managed Queueing Service
Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) is a cloud-native message queue for decoupling applications.
Key Features:Fully managed – No need for infrastructure setup.
Scales automatically – Handles millions of messages per second.
Message delay & visibility timeout – Controls when messages are processed.
Use Cases:
Microservices communication in cloud-native applications.
Asynchronous processing for event-driven workflows.
Handling unpredictable workloads with auto-scaling.
4. Webhooks – Event Notifications Without Polling
Webhooks enable real-time event notifications by sending HTTP callbacks when an event occurs.
Example: When a payment is completed, a webhook notifies the order fulfillment service instantly.
Key Features:Push-based mechanism – Avoids frequent polling.
Lightweight and easy to implement.
Works well for third-party integrations.
Use Cases:
Payment notifications (e.g., Stripe webhook for successful transactions).
CI/CD pipelines triggering builds after code commits.
CRM updates when customer data changes.
Choosing the Right Messaging Solution
Feature
Kafka
RabbitMQ
SQS
Webhooks
Best For
Event streaming
Message queuing
Cloud-native queuing
Real-time notifications
Durability
High
Medium
High
Low
Scalability
High
Medium
High
Medium
Ordering Guarantees
Yes (partitions)
Yes (FIFO queues)
Yes (FIFO)
No
Real-World Use Cases
1. E-Commerce Order Processing
RabbitMQ queues orders for background processing.
Kafka streams order events for analytics.
Webhooks notify users about order updates.
2. Log Processing & Monitoring
Kafka collects logs for real-time analysis.
SQS queues logs for later processing.
3. Financial Transactions & Fraud Detection
Kafka streams banking transactions to detect fraud.
RabbitMQ handles real-time trade execution.
Conclusion
Message queues and event-driven architectures improve scalability, efficiency, and responsiveness.
Kafka for high-throughput event streaming.
RabbitMQ for reliable message queuing.
SQS for cloud-native, managed queueing.
Webhooks for real-time event notifications.
Next, we’ll explore Fault Tolerance & High Availability – Failover Strategies, Self-Healing Systems.


